QGIS offers many tools for spatial data processing.
We will present some of the most common tools for processing vector data.
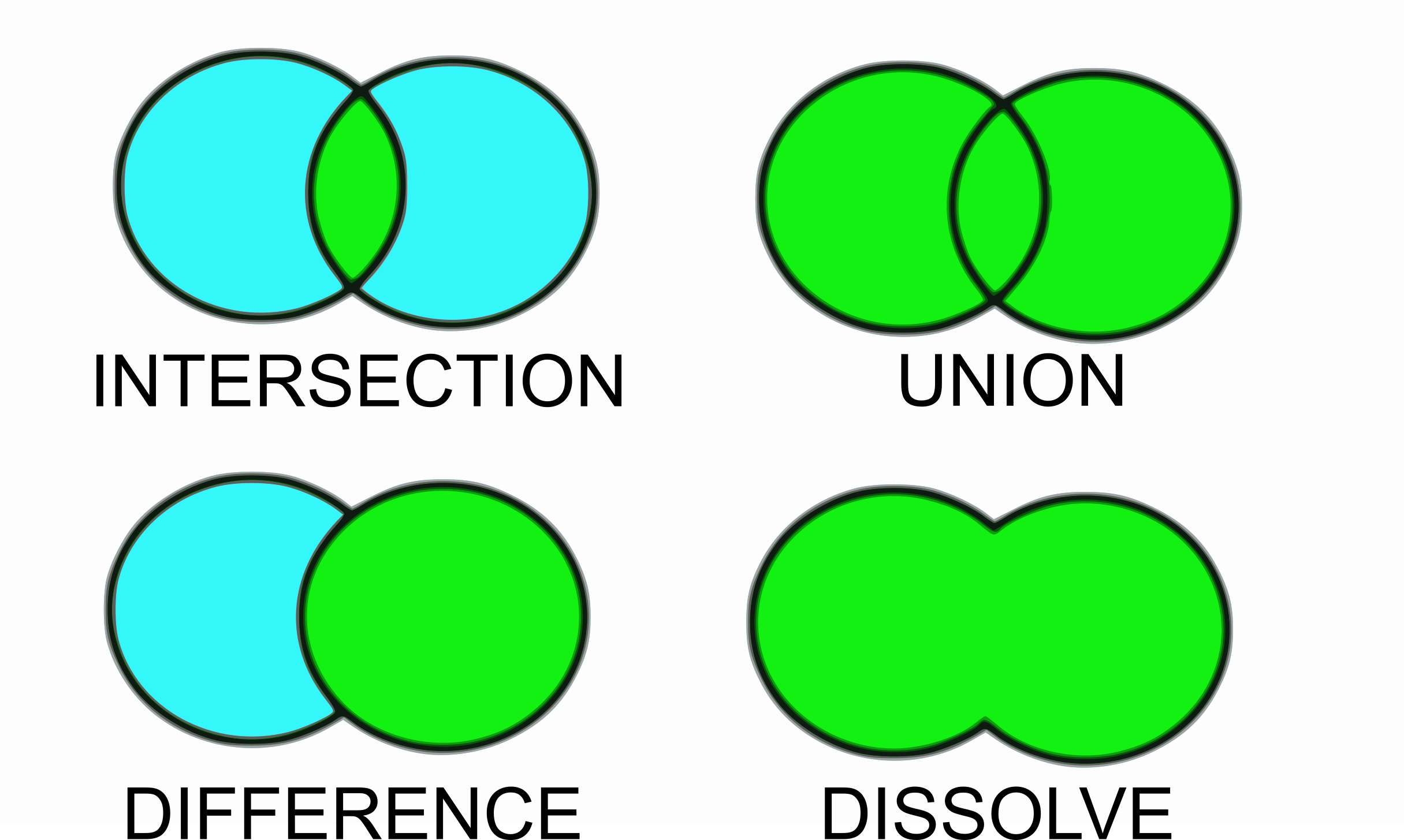
Logical operators:
- intersection
- union
- difference
- dissolve
- clip
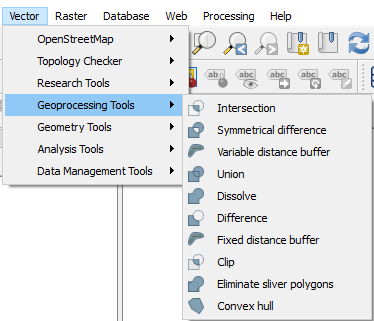
Logical operations can be found in the Geoprocessing tools:
We will show an example of the use of these tools in the case of data processing of population density data of municipalities and Cohesion regions.
Task: showing the population density of the municipalities of the cohesion region of Eastern Slovenia.
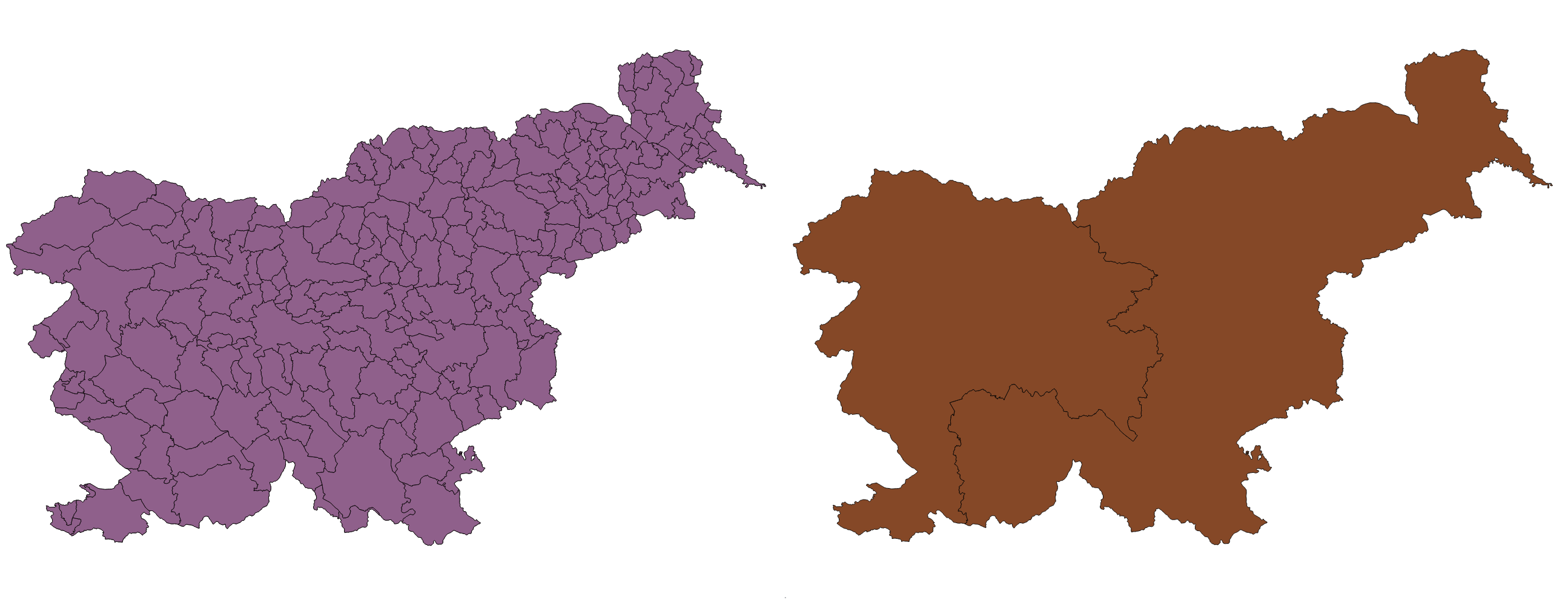
First, we delete the Cohesion region of Western Slovenia from the Cohesion regions layer. This is made with Toggle editing, marking the item we want to delete, pressing the delete button on the keyboard, and turn off editing. It is important that we are aware that the deletion of these elements also changes the input SHP data.
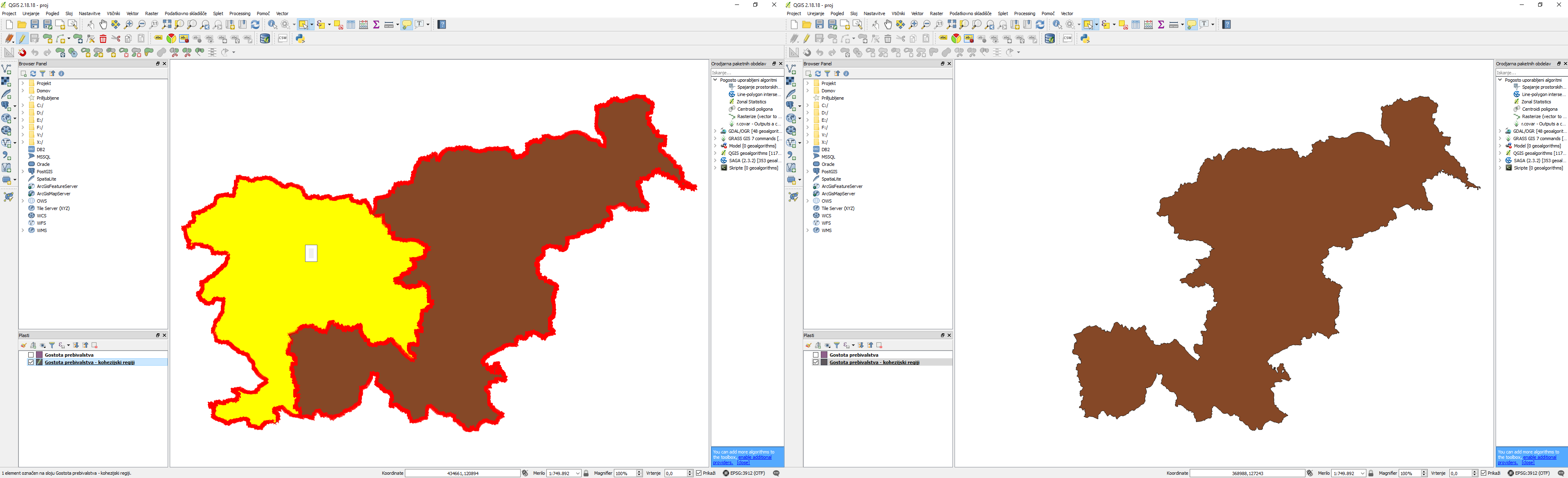
In order to gain all the municipalities from the cohesion region of Eastern Slovenia, we have to carry out an intersection between the layer of municipalities and the layer of cohesion regions of Eastern Slovenia. Select the Intersection tool and define the input and output data.
Geometry and data management tools:
- Merge vector layers: joining geometric data and their attribute tables
- Join attributes by location: merge data that has a common identifier
- Generate points
- Polygons to lines conversion and vice versa
- Topology Checker: checking that all geometries are topologically consistent
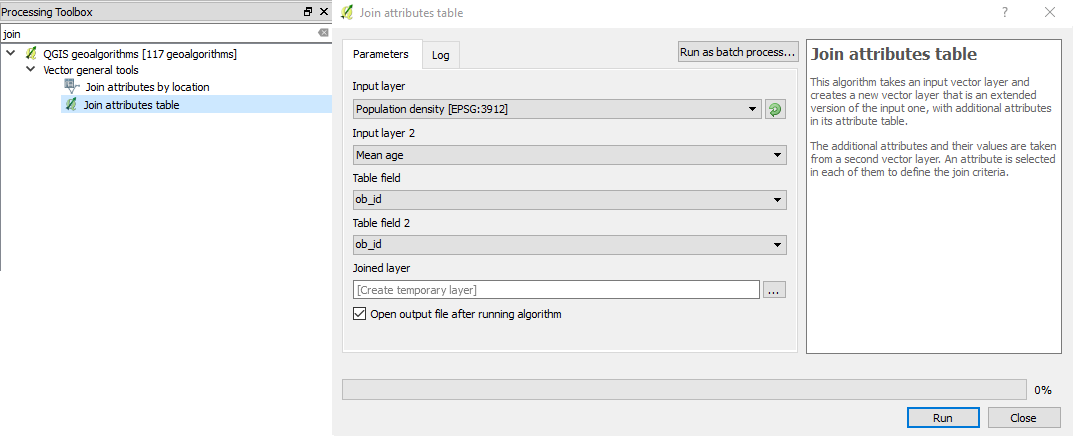
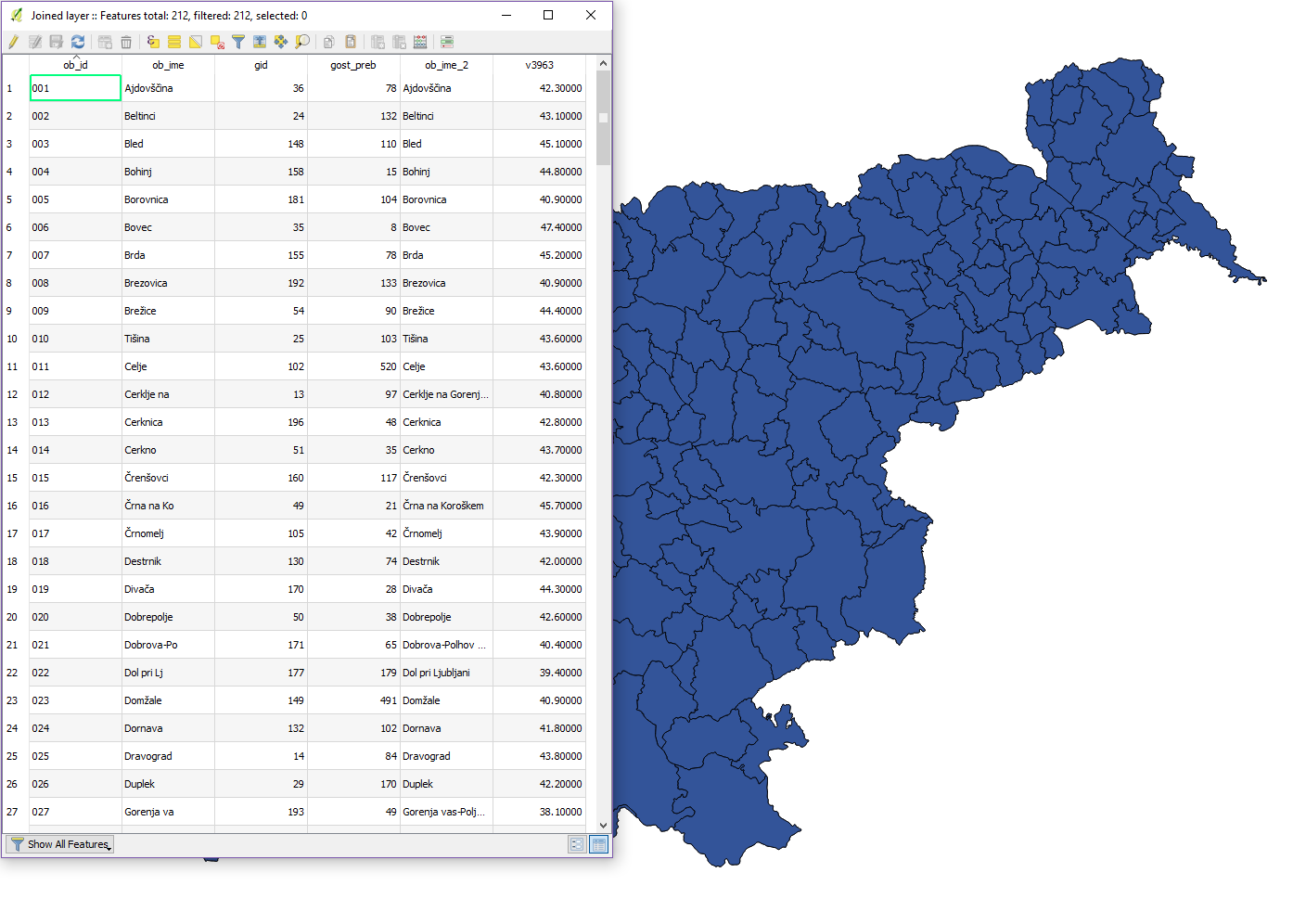
We’ll show you how to join attribute tables of SHP and CSV data that we imported
The data that we will join are population density (SHP - municipalities) and mean age (CSV - municipalities). The common identifier for performing the join is the ob_id field.
We will use the Join attributes table feature found in the Processing Toolbox.
In the next section we will show how to export data.